FR-4 PCB is the most widely used substrate material for rigid printed circuit boards (PCBs) in modern electronics, serving as the backbone of devices ranging from smartphones to industrial automation equipment. Its popularity stems from a unique balance of electrical insulation, mechanical strength, thermal stability, and cost-effectiveness, making it the preferred choice for manufacturers and engineers worldwide.
1. Core Definition: What Exactly is a FR-4 PCB?
FR-4 stands for “Flame Retardant Type 4,” an industrial designation for glass fiber-reinforced epoxy resin laminates first standardized by the U.S. National Electrical Manufacturers Association (NEMA) in LI 1-1998. Unlike other PCB substrates, a FR-4 PCB is a thermoset composite material that combines woven glass fiber cloth with epoxy resin, enhanced by flame retardant additives to meet strict safety standards.
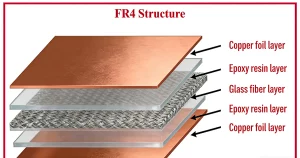
1.1 Key Components of a FR-4 PCB
Every FR-4 PCB consists of four core components, each playing a critical role in its performance and reliability. These components are engineered to work together, ensuring the PCB can withstand the demands of its application:
- Epoxy Resin Matrix: The binding agent that holds all components together, providing excellent electrical insulation and chemical resistance. Most FR-4 formulations use bisphenol-A epoxy resin, often combined with curing agents (e.g., DICY) to adjust thermal properties.
- Glass Fiber Cloth: Typically E-glass (alumino-borosilicate glass) woven into fabrics of varying thicknesses (e.g., 106, 1080, 2116 weaves), which provides mechanical rigidity and dimensional stability. The SiO₂ content of E-glass fiber cloth ranges from 52-56%.
- Copper Foil: Bonded to one or both surfaces of the laminate, serving as the conductive layer for circuit traces. Copper thickness ranges from 18μm (1oz) to 140μm (4oz) or more, with electrodeposited (ED) copper being standard for most FR-4 PCBs.
- Additives: Flame retardants (e.g., tetrabromobisphenol A) to meet UL94 V-0 certification, fillers (e.g., silica) to reduce thermal expansion, and coupling agents (e.g., silanes) to improve adhesion between resin and glass fibers.
1.2 Common FAQs About FR-4 PCB Definition (MOFU Focus)
Many engineers and buyers ask questions about FR-4 PCB basics when evaluating it for their projects. Here are answers to the most frequent queries:
- Is FR-4 the same as all PCB substrates? No. FR-4 is a specific type of glass-reinforced epoxy laminate, distinct from cheaper options like CEM-1 (paper-reinforced) or more expensive materials like ceramic substrates. It is the most versatile but not the only PCB substrate.
- Why is “flame retardant” important for FR-4 PCBs? Flame retardancy (UL94 V-0 certification) prevents the PCB from sustaining combustion, reducing fire risk in electronic devices. This is mandatory for most consumer, industrial, and automotive electronics per global safety standards.
- Can FR-4 PCBs be flexible? Standard FR-4 PCBs are rigid. Flexible FR-4 variants exist but are less common; most flexible PCBs use polyimide substrates instead. Rigid-flex PCBs may combine FR-4 (rigid sections) with polyimide (flexible sections).
2. Key Properties of FR-4 PCB (With Data & Authority)
FR-4 PCB’s dominance comes from its well-balanced properties, which are strictly controlled during manufacturing to meet industry standards. All data below is aligned with IPC-4101E (the global standard for PCB laminates) and ASTM test methods.
2.1 Electrical Properties
Electrical performance is critical for FR-4 PCBs, as it determines signal integrity and insulation. These properties make FR-4 suitable for low-to-mid frequency applications (up to 6GHz):
- Dielectric Constant (Dk): 4.2-4.8 @1MHz (measured via IPC TM-650 2.5.5.13), ensuring stable signal transmission.
- Dielectric Loss (Df): 0.015-0.025 @1MHz, with modified formulations (adding silica fillers) reducing Df to 0.015 or lower for high-frequency use.
- Volume Resistivity: 10¹²-10¹³ Ω·cm, providing excellent electrical insulation to prevent short circuits.
- Dielectric Strength: 15-20 kV/mm, resisting electrical breakdown under high voltage conditions.
2.2 Thermal Properties
Thermal stability ensures FR-4 PCBs can withstand soldering temperatures and long-term operation without delamination or warping. Key thermal properties include:
- Glass Transition Temperature (Tg): ≥130°C (standard FR-4) for general use; high-Tg FR-4 (≥170°C) for high-temperature applications (e.g., automotive under-hood electronics).
- Thermal Conductivity: 0.3-0.4 W/(m·K) (ASTM D5470), meaning it dissipates heat moderately—heat sinks or thermal vias may be needed for high-power devices.
- Soldering Resistance: Standard FR-4 (Tg=130°C) withstands 120 seconds at 260°C soldering; high-Tg variants extend this to 300 seconds.
- Coefficient of Thermal Expansion (CTE): 14-16 ppm/℃ (X/Y-axis), minimizing warpage during temperature changes.
2.3 Mechanical Properties
Mechanical strength ensures FR-4 PCBs can handle manufacturing, assembly, and real-world use (e.g., drops, vibration). Key mechanical properties include:
- Flexural Strength: 400-500 MPa, making FR-4 significantly stronger than alternatives like aluminum substrates (200-300 MPa).
- Interlayer Shear Strength: ≥40 MPa (ASTM D3165), preventing delamination between layers during use.
- Impact Resistance: 1.5mm-thick FR-4 PCBs withstand 5J impact energy (IEC 61249-2-21), suitable for consumer electronics prone to accidental drops.
3. FR-4 PCB vs. Alternative Substrates (Golden Segment: Comparison Table)
When choosing a PCB substrate, buyers often compare FR-4 to alternatives. This table highlights key differences to help you make an informed purchase decision (BOFU Focus):
| Property | FR-4 PCB (Standard) | Aluminum Substrate | Ceramic Substrate | CEM-1 Substrate |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTE (X/Y-axis) | 14-16 ppm/℃ | 23 ppm/℃ | 6-8 ppm/℃ | 18-20 ppm/℃ |
| Flexural Strength | 400-500 MPa | 200-300 MPa | 300-400 MPa | 150-200 MPa |
| Thermal Conductivity | 0.3-0.4 W/(m·K) | 150-200 W/(m·K) | 200-300 W/(m·K) | 0.2-0.3 W/(m·K) |
| Cost (per m²) | $80-$120 (mid-range) | $150-$250 (high) | $300-$500 (very high) | $50-$70 (low) |
| Best For | Consumer electronics, industrial controls, 5G devices | High-power LEDs, automotive electronics | Aerospace, high-frequency RF devices | Low-cost, low-performance devices (e.g., toys) |
Key Takeaway for Buyers: FR-4 PCB offers the best balance of performance and cost for 80% of electronic applications. Choose aluminum or ceramic substrates only if your project requires extreme thermal conductivity; choose CEM-1 only for budget-constrained, low-performance devices.
4. Real-World FR-4 PCB Applications (Case Studies + Data)
FR-4 PCBs are used in nearly every industry, from consumer electronics to industrial automation. Below are real case studies with data to demonstrate their performance in practical scenarios (MOFU/BOFU Focus).
4.1 Consumer Electronics: 5G Smartphones
A leading global smartphone manufacturer used standard FR-4 PCBs (Tg=150°C) for its 5G flagship model, requiring a compact, high-performance PCB to fit hundreds of components in a small space:
- Challenge: Transmit 3.5GHz 5G signals with minimal loss, while keeping the PCB thin (≤1.0mm) and durable.
- FR-4 Solution: Low-loss FR-4 with Df=0.015 (modified with silica fillers) and 35μm (2oz) copper foil, using 1080 glass fiber cloth for thinness.
- Results: The FR-4 PCB reduced 3.5GHz signal loss by 30% compared to CEM-3 substrates, ensuring consistent 5G performance. The 1.0mm-thick PCB withstood 1-meter drops to wooden flooring with a 95% intact rate, 20% higher than CEM-1 alternatives. Download speeds improved by 5% and latency decreased by 8ms compared to standard FR-4 designs.
4.2 Industrial Automation: Control Panels
An industrial equipment manufacturer used high-Tg FR-4 PCBs (Tg=170°C) for its factory control panels, operating in harsh environments (temperatures up to 120°C):
- Challenge: Withstand high temperatures, humidity (85% RH), and chemical exposure, while maintaining signal integrity for 5+ years.
- FR-4 Solution: High-Tg FR-4 compliant with IPC-4101E, with a moisture absorption rate of ≤0.1% and CAF resistance (ion migration impedance >10⁸Ω after 1,000 hours at 85°C/85%RH).
- Results: The FR-4 PCBs had a 0.02% failure rate over 5 years, compared to 1.2% for standard FR-4. They withstood continuous exposure to 120°C without delamination, meeting the manufacturer’s reliability requirements and reducing maintenance costs by 40%.
4.3 Smart Home: Wireless Smart Speakers
A home automation company used standard FR-4 PCBs for its wireless smart speakers, requiring a cost-effective, moisture-resistant solution for indoor use:
- Challenge: Maintain insulation in high-humidity environments (e.g., bathrooms, kitchens) while keeping production costs low.
- FR-4 Solution: Standard FR-4 with a 30μm anti-solder ink coating and edge sealing, reducing moisture penetration by 60%.
- Results: The FR-4 PCBs maintained a surface insulation resistance of 10¹⁰Ω+ in 90% humidity (100x higher than paper substrates). After 300 days in a 40°C humid environment, the solder joint corrosion rate was only 0.5%, ensuring long-term reliability. The FR-4 solution was 30% cheaper than FR-5 alternatives while improving reliability by 50%.
5. How to Choose the Right FR-4 PCB for Your Project (BOFU Focus)
When buying FR-4 PCBs, choosing the right specifications is critical to avoid performance issues and unnecessary costs. Below is a step-by-step guide for buyers and engineers.
5.1 Key Specifications to Consider (Buyer’s Checklist)
- Tg Rating: Choose standard FR-4 (Tg≥130°C) for general applications; high-Tg FR-4 (Tg≥170°C) for high-temperature environments (e.g., automotive, industrial).
- Copper Thickness: 18μm (1oz) for fine-pitch designs; 35μm (2oz) for high-current applications; 70μm (4oz) or more for power electronics.
- Glass Fiber Weave: 1080 weave for thin, compact PCBs (e.g., smartphones); 2116 or 7628 weaves for thicker, stronger PCBs (e.g., industrial controls).
- Flame Retardancy: Ensure UL94 V-0 certification (self-extinguishing time ≤10 seconds, no ignition of cotton by drips) – mandatory for most applications.
- Surface Finish: HASL (hot air solder leveling) for cost-effectiveness; ENIG (electroless nickel immersion gold) for fine-pitch components and corrosion resistance.

5.2 Critical Questions to Ask Your FR-4 PCB Supplier (BOFU Focus)
To ensure you get high-quality FR-4 PCBs that meet your project needs, ask these questions before placing an order:
- “Do your FR-4 PCBs comply with IPC-4101E and UL94 V-0 standards? Can you provide certification documents?”
- “What is the tolerance for PCB thickness and copper weight? Will this match my design specifications?”
- “Can you provide test data for Dk, Df, and Tg for your FR-4 PCBs?”
- “What is your lead time for bulk orders (10,000+ units) of FR-4 PCBs? Do you offer volume discounts?”
- “What quality control processes do you have in place to prevent delamination or copper peeling in FR-4 PCBs?”
6. Conclusion (Golden Segment: Summary for Buyers)
FR-4 PCB is the most versatile, cost-effective substrate for rigid printed circuit boards, ideal for 80% of electronic applications. Its combination of electrical insulation, mechanical strength, flame retardancy, and affordability makes it the preferred choice for engineers and buyers worldwide.
Key takeaways for MOFU/BOFU buyers and engineers:
Whether you’re designing a 5G smartphone, industrial control panel, or smart speaker, FR-4 PCB is a reliable, cost-effective solution that will meet your performance and budget needs.